Prostatitis is an inflammation of a person's prostate gland.The prostate is located directly below the bladder and chestnut size.It takes the first part of the urethra around and extends to the so -called pelvic floor consisting of muscles.
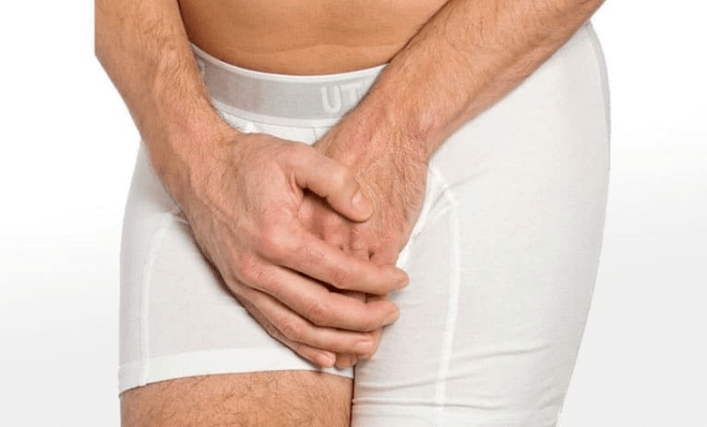
It results in prostate secretion, which includes PSA and sperm.The PSA makes the ejaculate more liquid.Spermin is important for sperm mobility.
Prostatitis primarily involves severe pain in the perineum and anal region.In addition, symptoms such as urination, urination, pain and ejaculation pain in prostate inflammation.
Prostate is relatively often affected by inflammation.The likelihood of prostate infection increases with age.Studies show that most cases are 40-50 years old.
Prostatitis syndrome
At the same time, the expanded understanding of the term prostatitis appeared in medicine.The so -called prostatitis syndrome summarizes a number of complaints in the human pool, which is usually an unknown cause.The term "prostatitis syndrome" summarizes various clinical paintings:
- Acute bacterial prostatitis
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis
- Chronic pelvic pain is an inflammatory and non -inflammatory syndrome
- Asymptomatic prostatitis
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis
Acute prostatitis is caused by bacteria.Bacteria either pass through the blood to the prostate or spread from the bladder or urethral bacterial infection to the prostate.Acute prostatitis is usually a severe general condition with severe pain during fever and chills.
Chronic prostatitis can develop from acute: if the prostate gland and repeated microbes have inflammation in the urine for more than three months, then the so -called prostate express or ejaculate, then it is chronic inflammation.
Bacterial prostatitis.This is less lightning speed than acute prostatitis.Although chronic inflammation of the prostate gland causes pain during urination and perhaps the feeling of perineum pressure, the complaints are usually not expressed as in acute prostatitis.
Chronic pelvic pain -syndrome (abacterial prostatitis)
In most cases, prostate infections, bacteria are not detected in urine, prostate or disease as the cause of the disease.The prostatitis trigger is still unclear.Doctors call it a chronic pelvic pain.
In such cases, however, leukocytes are often detected as an expression of inflammation in the prostate gland.To distinguish this, the other form of the disease, in which neither bacteria nor leukocytes are detected.Chronic pelvic pain syndrome is the most common form of prostatitis.
Asymptomatic prostatitis
In rare cases, asymptomatic prostatitis occurs.With this form of prostatitis, although there are signs of inflammation, there is no pain or other symptom.Symptom -free prostatitis is usually detected randomly, for example as part of infertility.
Prostatitis: Symptoms
Inflammation of the prostate can cause various symptoms of prostatitis.Although the symptoms of acute prostatitis can be very severe and may cause severe malaise, they are generally slightly weaker in chronic prostatitis.
Acute Prostatitis: Symptoms
Acute prostatitis is often an acute disease in which patients suffer from fever and chills.The urination causes burning pain and the flow of urine is noticeably reduced due to the prostate edema.Because the victims can only distinguish a small amount of urine, they have a constant frequency of urinary urination and often have to go to the toilet.Other symptoms of prostatitis include bladder, pelvic pain and back pain.Pain can also occur during or after ejaculation.
Chronic prostatitis: symptoms
Prostatitis with chronic pathways usually causes less severe symptoms than acute inflammation of the prostate.Symptoms such as fever and chills are usually completely absent.Symptoms, such as perineum or lower abdomen, a darkening of blood from blood in the sperm or urine is characterized by chronic inflammation of the prostate. The symptoms of chronic bacteria and chronic abacterial prostatitis are not different.
Complications of prostatitis
The most common complication is the prostate abscess.The prostate is the inflammation of the inflammation, which should usually be opened and emptied by cutting.
As a further complication of prostate inflammation, inflammation may apply to nearby structures, such as the appendix of the testicles or testicles.It is also suspected that chronic prostatitis is related to the development of prostate cancer.
Prostatitis: Causes and risk factors
Bacterial prostatitis: causes
Only ten percent of the cases of prostatitis are caused by the bacterium of the prostate.Bacteria can enter the prostate with blood or from adjacent organs such as bladder or urethra, where they can lead to an inflammatory reaction.
The Escherichia Coli bacterium, which is primarily in the human gut, is the most common cause of prostatitis.Klebsiella, enterococcus or mycobacteria can also cause prostatitis.Bacterial prostatitis can be caused by sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydial or trichomonas and gonorrhea.
In chronic prostatitis, prostate bacteria have avoided the unclear way of protecting the human immune system.This allows microbes to constantly colonize the prostate.Antibiotics are relatively weak in the tissue of the prostate gland, which may be another reason for the survival of bacteria in the prostate gland.
Chronic pelvic pain -syndrome: reasons
The exact causes of chronic pelvic syndrome have not yet been completely investigated.Scientists have designated many theories, all of which sound incredible, but they have not yet been clearly proven.In some cases, the genetic material of previously unknown microorganisms was found in the pool.Therefore, the pelvic pain syndrome may be caused by microorganisms that cannot be grown in the laboratory and therefore not detected.
Another possible cause of chronic pelvic pain is the disorders of the bladder.Due to impaired drainage, the volume of the bladder increases, thus pushing the prostate.This pressure eventually damage the prostate tissue, causing inflammation.
In many cases, however, the cause of chronic pelvic pain cannot be clearly proven.Doctors then talk about idiopathic prostatitis.
Anatomical reasons
In rare cases, prostatitis is caused by narrowing of the urinary tract.If the urinary tract narrows, the urine accumulates and, if entered the prostate, can cause inflammation.This narrowing can be caused by tumors or so -called prostate stones.
Mental reasons
Recently, more and more psychological reasons have been discussed on prostatitis.In particular, chronic pelvic pain with non -inflammatory syndrome is likely to be a mental starter.The exact mechanisms are not yet known.
The risk factors of the formation of prostatitis
Some men particularly endanger the development of prostate infection.This includes, for example, men suppressed by the immune system or suppressed by the immune system.In addition, main diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, can contribute to the development of prostatitis: increased blood sugar levels in diabetics often lead to increased sugar levels.In urine, abundant sugar content can provide good growth conditions for bacteria, facilitating urinary tract infections.
Another risk factor for the development of prostatitis is the bladder feed.The introduction of the catheter can cause small fracture of the urethra through the urethra through the urethra and damage to the prostate gland.In addition, as with all foreign bodies, bacteria can settle on the bladder and form a biofilm called SO.As a result, bacteria can rise to the bladder along the urethra and lead to prostate infection.
Prostatitis: Tests and Diagnostics
The general practitioner may have medical history, but if you suspect prostatitis, you will direct you to the urologist.This performs a physical examination.In the case of suspected prostatitis, this is usually the so -called digital rectal test.Nevertheless, this study does not provide clear evidence of inflammation of the prostate, but only confirms suspicion.A laboratory test can be performed to detect bacterial prostatitis
Finger test
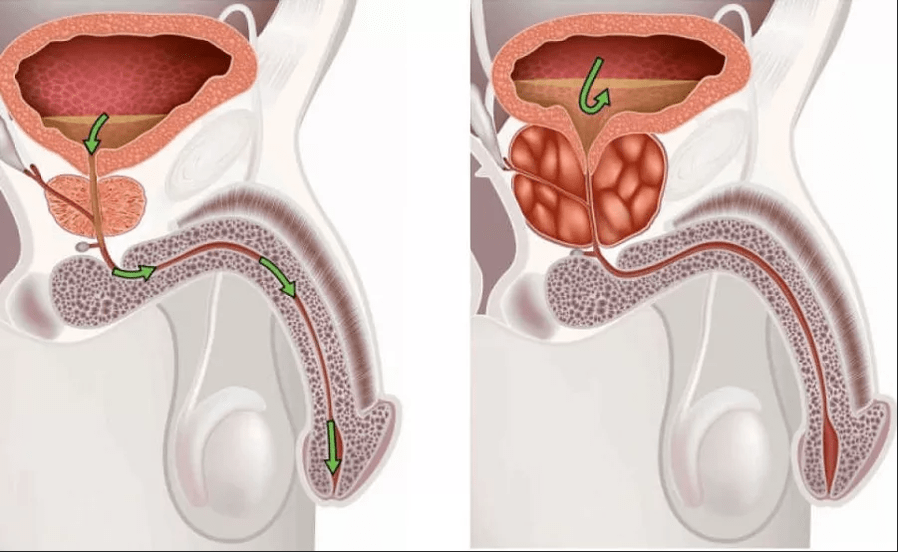
Because the prostate gland is directly bounded by the rectum, it is palpable in the rectum.This digital rectal test is performed on an outpatient basis and without anesthesia, usually painlessly.The patient is asked to lie down with bent legs.With a lubricant, the doctor slowly inserts your finger into the anus and scans the prostate and adjacent organs.Examine the size and sensitivity of the pain of the prostatamine gland.
Laboratory test
In most cases, urine analysis is performed to identify potential pathogens.The standard method is the SO pattern of four glasses.Here, erturine, mitelstrahlurine, prostatexprimat and urin are tested after prostate massage.As Prostataxprimat called, doctors call the prostate secretion.This is achieved by the doctor with light pressure on his prostate, for example on palpation.The ejaculate can also be examined for pathogenic microorganisms and signs of inflammation.
Further research
Ultrasound scanning of the rectum can be used to determine exactly where the inflammation is and how far it spreads.One of the important goals of the study is to exclude other diseases with similar symptoms.
In order to exclude existing violation of urinary drainage is caused by narrowing of the urethra, the urinary tract is measured.Normal urine flow is 15-50 milliliters per second, while urine flow is ten milliliters per second or less, with high probability of the urethra obstruction.
Prostatitis: Treatment

Medication
Acute bacterial prostatitis is treated with antibiotics.In mild cases, the antibiotic dose is sufficient for about ten days.In the case of chronic prostatitis, the medicine should be taken longer.Depending on the pathogenic microorganisms, the active materials of luxacin, ciprofloxacin, azithromycin, erythromycin or doxi cycle are suitable.Even if the symptoms are gone, antibiotics must be continued by appointing the doctor.
In addition, asymptomatic prostatitis is treated with antibiotics.
If there is chronic abacterial prostatitis, antibacterial therapy is generally ineffective.With the inflammatory syndrome of chronic pelvic pain, even though they do not prove the presence of the pathogen, an examination is performed using antibiotics, as it is sometimes possible to improve.However, with the non -inflammatory syndrome of chronic pelvic pain, antibiotic treatment is not recommended.
Further therapeutic approaches of chronic abactitis prostatitis are the so-called 5A reductase inhibitors such as fineride or dutasteride, pentosan polyisulfate and herbal medicines such as chvercetin or dust extract.If the improvement is not achieved, medication therapy is supplemented with physiotherapy.It is recommended here for physiotherapy exercises, the practice of pelvic floor muscles or the prostate regular massage.
In addition, symptomatic treatment can help relieve the acute symptoms of the prostate infection.Anesthetic drugs can be prescribed for severe pain.In addition, the rear or lower abdominal heating pads and heating pads help relax the muscles.This often relieves pain with prostate inflammation.
Relapse
The frequency of prostatitis relapse is generally very high.The victims are approx.23 % are subject to the second episode of the disease after a disease, 14 % suffer from three and 20 percent -even for four or more.To reduce the risk of relapse, avoid wearing wet clothing during or after using prostatitis, hypothermia or bubbles such as black tea or coffee.This reduces the risk of cystitis and therefore prostatitis.However, using these methods cannot reliably prevent bacterial prostatitis.
The prediction of prostatitis depends on the cause of the inflammation and on the other hand how quickly the proper treatment begins.
In acute bacterial prostatitis, which is treated as soon as possible with antibiotic treatment, prognosis is generally good.Taking antibiotics, pathogens die, which usually prevents the transition to chronic prostatitis.
Patients with acute prostatitis are approx.60 % no longer have symptoms in six months and approx.20 % develop at chronic prostatitis.Treatment and prognosis are harder here.In many cases, intermittent episodes of the disease are accompanied by those who have suffered for years.
Chronic prostatitis usually requires great patience from the victims.Very often, a long course can be a serious psychological burden.
Suffering patients should seek professional help as the mental health situation has a huge impact on the prediction of prostatitis.